Mancozeb stands tall among the vital fungicides employed in modern agriculture. Whether you’re a farmer tending to vast fields or a gardener nurturing plants, the chances are that you’ve crossed paths with this powerful tool in the fight against fungal diseases. But what exactly is mancozeb? Why is it revered and reviled in equal measures? Let’s embark on a journey to unravel the mysteries of mancozeb.
Chemical Composition and Properties
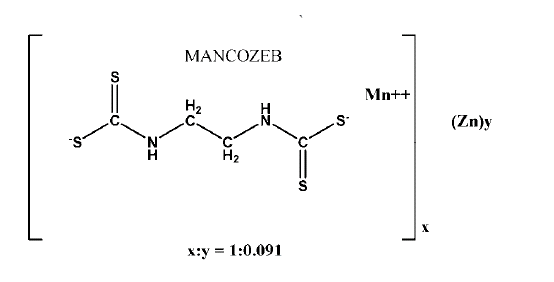
Mancozeb is a coordination complex of manganese, zinc, and ethylene bis(dithiocarbamate). It falls under the category of dithiocarbamate fungicides, known for their protective action against various fungal pathogens.
Chemical Structure
The chemical structure of mancozeb consists of two manganese ions and one zinc ion that are coordinated with the nitrogen atoms of ethylene bis(dithiocarbamate). This unique structure gives mancozeb its distinct fungicidal properties.
Physical and Chemical Properties
Mancozeb is a grayish-yellow powder with a slightly musty odor. Its insolubility in water makes it suitable for use in wettable powders, flowable concentrates, or dust formulations. Here are some key properties of mancozeb:
- Solubility: Practically insoluble in water and most organic solvents
- Molecular weight: 266.32 g/mol
- pH: Neutral in aqueous solution
- Stability: Stable under normal storage conditions but decomposes at elevated temperatures
These properties make mancozeb a versatile and effective fungicide for a wide range of applications. Its stability and compatibility with other agricultural chemicals contribute to its widespread use in modern farming.
Applications in Agriculture
Mancozeb is a key player in the protection of crops against a plethora of fungal diseases. Its broad-spectrum action makes it suitable for various agricultural applications.
Usage in Different Crops
From the vast fields of corn to the delicate vines of grapes, mancozeb is a friend to farmers. Here’s a list of some common crops where mancozeb is frequently applied:
Mancozeb’s ability to thwart diseases like blight, rust, and mildew makes it indispensable in modern agriculture. Its preventative action shields crops from potential devastation, ensuring healthier plants and bountiful harvests.
Environmental and Health Concerns
The widespread usage of mancozeb has raised questions about its impact on both the environment and human health. While beneficial in controlling fungal diseases, certain aspects need careful consideration.
Ecological Impact
Mancozeb’s potential impact on non-target organisms has been a matter of ongoing study. Its effects on aquatic life, birds, and beneficial insects have been documented. Here’s a look at some concerns:
- Potential toxicity to fish and aquatic invertebrates
- Possible harm to beneficial soil microorganisms
- Concerns over bioaccumulation in the food chain
Proper application and adherence to guidelines can minimize these risks, but awareness and continued research are key to understanding the full ecological impact of mancozeb.
Health Considerations
Mancozeb, like many chemical fungicides, must be handled with care. Potential health risks are associated with improper handling or prolonged exposure:
- Skin and eye irritation
- Respiratory issues if inhaled
- Long-term exposure may have reproductive or developmental effects
These concerns necessitate strict adherence to safety guidelines, proper training, and the use of protective equipment when handling or applying mancozeb. Responsible usage and awareness of potential risks are crucial in ensuring safety.
Regulatory Perspectives
The complex nature of mancozeb’s impact on the environment and human health has led to varied regulatory perspectives across the globe. Different nations have adopted different stances, reflecting the balance between agricultural needs and safety considerations.
Global Regulations
Mancozeb has faced varying degrees of regulation worldwide. While some countries continue to allow its use under specific guidelines, others have implemented partial or complete bans. This disparity in regulations is a testament to the ongoing debate surrounding its safety and efficacy:
- European Union: Phased out due to potential risks to human health and the environment
- United States: Registered for use with specific guidelines and restrictions
- Other countries: Varying regulations depending on local agricultural needs and safety assessments
These regulatory landscapes underline the need for a unified approach to assessing and managing mancozeb, reflecting both its importance in agriculture and the necessity for environmental stewardship and human well-being.
Alternatives and Future Perspectives
The complex world of mancozeb doesn’t end with its current applications and challenges. As the agriculture industry evolves and the understanding of environmental and health impacts deepens, the quest for alternatives and future trends becomes imperative.
Alternative Fungicides
With increasing scrutiny and regulations, the search for alternatives to mancozeb has gained momentum. Several other fungicides and organic options are being explored:
- Biofungicides: Utilizing microorganisms or botanical extracts to combat fungal diseases.
- Other Synthetic Fungicides: New chemicals with targeted action and potentially lesser environmental impact.
- Integrated Pest Management (IPM): A holistic approach combining biological, physical, and chemical methods to control diseases.
These alternatives provide promising avenues for sustainable agriculture, balancing the need for crop protection with ecological considerations.
Future Research and Trends
The dynamic field of fungicide research and the shifting landscape of regulations have paved the way for innovative approaches in understanding and utilizing mancozeb. Future trends might include:
- Development of more targeted and environmentally friendly formulations
- Advanced risk assessment models to evaluate potential impacts
- Increased investment in biological and non-chemical alternatives
- Enhanced farmer education and stewardship programs for responsible usage
These trends represent a progressive shift towards a more responsible and innovative approach to handling mancozeb and other fungicides. The future holds opportunities for growth and improvement, aligning with global goals of sustainable agriculture and environmental protection.
Conclusion
The story of mancozeb is a tale of contrasts. A tool of immense importance in the agricultural world, yet a subject of scrutiny and regulation. Its role in safeguarding crops from fungal diseases is undeniable, but the need for responsible usage, awareness, and continued exploration of alternatives is equally paramount. Mancozeb’s journey reflects the broader challenges and opportunities in modern agriculture—a delicate balance between human needs, technological advancement, and environmental stewardship. As we look towards the future, the lessons learned from mancozeb will guide us in cultivating a path that nourishes both our planet and its people.
